Brain Tumor Care > Meningioma
As a patient, you'll have access to advanced and highly individualized medical, surgical, and minimally invasive options, as well as promising new therapies for treating complex adult brain tumors. We discuss meningioma cases with your hospital's multidisciplinary tumor board, a team of specialists that shares opinions and then synthesizes them into a recommended treatment strategy for you. Treatment options include skull base surgery, minimally invasive keyhole and endoscopic surgery, radiotherapy, and careful observation. Mayfield treats about 400 patients each year with meningioma brain tumors.
About meningiomas
A meningioma is a tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and slow growing; however, some can be malignant. Symptoms typically appear gradually and vary depending on the tumor location. Because of their slow growth, not all meningiomas need to be treated immediately.
Meningioma treatments:
In the past 5 years, Mayfield has seen 2,971 patients with meningiomas and performed 542 procedures — making Mayfield a high-volume treatment program.1 In context, nearly a quarter of people newly diagnosed with a meningioma in Ohio2 seek care at Mayfield, many of which are observed.
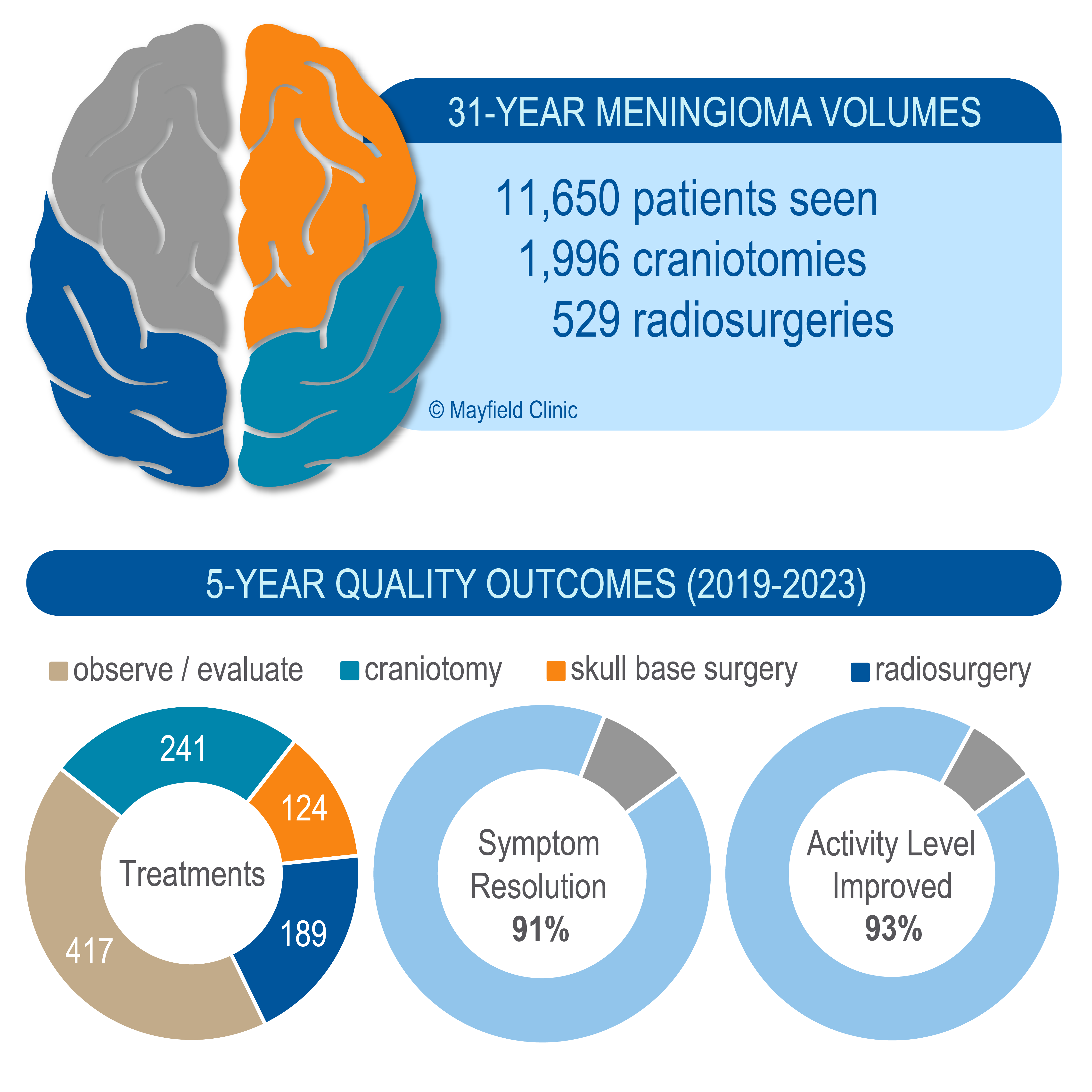
Symptom resolution (seizure, headache, cranial nerve function) are the main goals of surgery and are highly dependent on tumor location (convexity vs. skull base). Consistent with the literature3,4, Mayfield's patients have 91% resolution of their symptoms and 93% have improved or full activity level.
Mayfield participates in meaningful large-scale clinical studies by working with national research consortiums including the International Radiosurgery Research Foundation (IRRF) and the NeuroPoint Quality Outcomes Database (QOD). These efforts establish benchmarks and generates data to improve the quality of care for all brain tumor patients.

- Asuzu DT … Warnick RE, et al. Clinical and radiologic outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for meningiomas in direct contact with the optic apparatus: an international multicenter study. J Neurosurg. 2021 Sep 24;136(4):1070-1076.
- Bunevicius A … Warnick RE, et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Olfactory Groove Meningiomas: An International, Multicenter Study. Neurosurgery. 2021 Oct 13;89(5):784-79.
- Shepard MJ … Warnick RE, et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Atypical (World Health Organization II) and Anaplastic (World Health Organization III) Meningiomas: Results From a Multicenter, International Cohort Study. Neurosurgery. 2021 Apr 15;88(5):980-988.
- Gozal YM, et al. Repeat Resection of a Cavernous Malformation of the Optic Nerve/Chiasm via a Frontotemporal Approach: 2-Dimensional Operative Video. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2020 May 1;18(5):E169-E170.
- Lee KD … McPherson CM, et al. Atypical meningiomas: is postoperative radiotherapy indicated? Neurosurg Focus. 2013 Dec;35(6):E15.












